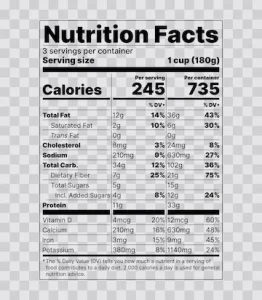
Nutrition labels on packaged food items often contain a number of carbohydrates. But how much of each type of carbohydrate should you be eating?
There are six types of carbohydrate on nutrition labels: dietary fiber, sugar, starches, sugars, maltose and glucose. All of these carbohydrates provide different nutritional benefits and can affect your blood sugar levels in different ways. Here’s a look at how each one affects your blood sugar levels and what to take into account when calculating how much to eat.
Contents
- 1 What are carbohydrates?
- 2 Carbohydrates in foods
- 3 How do carbohydrates affect our body?
- 4 The glycemic index and the glycemic load
- 5 Thecarbohydrates in popular food items
- 6 The benefits of consuming carbohydrates
- 7 What are Carbohydrates?
- 8 Types of Carbohydrates
- 9 How Carbohydrates Are Used In The Body
- 10 What Are the Nutrition Facts for Foods?
- 11 Why Is There a Difference in Calories on the Label for Carbohydrates?
- 12 What to Do If You Think You’re Having Too Much Sugar or Carbohydrates in Your Diet?
- 13 Conclusion
What are carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are a type of food that provides energy for the body. They are found in many foods, including fruits, vegetables, grains, and milk.
The most common types of carbohydrates are sugar, starches, and fiber.
Sugar is made of simple sugars such as glucose and fructose. Starches are chains of carbon atoms that are long and thin. Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that is found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly a carbohydrate will raise blood sugar levels after it is eaten. High-glycemic index foods tend to be more fattening than low-glycemic index foods.
There are two types of carbohydrates: simple and complex. Simple carbohydrates include sugar and starches, while complex carbohydrates include fiber and other nutrients. Complex carbohydrates are important because they give the body longer-lasting energy than simple carbs.
How do carbohydrates affect weight?
When you eat carbohydrates, your body converts them into glucose. Glucose is the main source of energy for the body. The more carbohydrates you eat, the more glucose your body will create. This means that eating large amounts of simple carbs
Carbohydrates in foods
There’s a lot of confusion around what counts as a “carbohydrate” on nutrition labels. Some people think that all carbs are bad for you, while others believe that some types of carbs are better than others. Here’s a quick overview of what carbohydrates are and what they do in your body.
Carbohydrates are one of the three main food groups, along with proteins and fats. They’re essential for energy production and help to keep you feeling full after eating. Most carbohydrates are found in plant-based foods, like fruits, vegetables, and grains.
There are two types of carbs: simple and complex. Simple carbs consist of only sugar molecules and don’t provide much nutritional value. Complex carbs have more than one sugar molecule and offer more nutrients, including fiber.
Some experts believe that complex carbs are better than simple carbs when it comes to staying healthy. They say that complex carbs can help you lose weight because they keep you feeling fuller longer and provide more nutrients than simple carbs. However, there is still some controversy around this topic so you should talk to your doctor before changing your eating habits based on what you read online.
How do carbohydrates affect our body?
Carbohydrates are a type of food that our body uses for energy. Our body can either use these carbohydrates for immediate energy or store them for later use. When we eat carbohydrates, our body breaks them down into sugar molecules. Our cells then use these sugar molecules for energy. There are two types of carbohydrates, simple and complex. Simple carbohydrates are found in things like bread, pasta, and candy. Complex carbohydrates are found in things like fruits, vegetables, and legumes. Both types of carbohydrates have their own benefits and drawbacks.
Simple carbohydrates provide quick energy but can cause spikes in blood sugar levels. This can lead to weight gain if we consistently eat these types of foods. Complex carbohydrates are more beneficial because they cause gradual rises in blood sugar levels. This helps to keep our blood sugar levels stable and prevents us from getting into energy crash mode. However, complex carbs can also cause us to feel fuller longer so they’re not always the best option when it comes to weight loss.
Overall, carbs play an important role in our body’s metabolism and should be included in our diet in some form or another. It’s important to balance out the benefits and drawbacks of each type of carbohydrate
The glycemic index and the glycemic load
Carbohydrates on a nutrition label may seem like they’re adding up, but they don’t have to. The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly a carbohydrate raises blood sugar levels after it’s eaten. Foods with a high GI are quickly absorbed and cause a surge in blood sugar, while low-GI foods take longer to digest and cause a gradual increase in blood sugar.
The glycemic load (GL) is another way to measure how fast a carbohydrate raises blood sugar levels. It takes into account both the GI and the number of calories in a food. A food with a high GL will cause a much larger blood sugar spike than one with a low GL. But remember: Just because something has a high GL doesn’t mean it’s bad for you. In fact, many foods with high GLs are also rich in important nutrients and fiber.
Thecarbohydrates in popular food items
Carbohydrates are one of the four main food groups and account for around 35-45% of a person’s total daily caloric intake. While many people believe that carbohydrates add up quickly in the body, the truth is that they don’t. Carbohydrates are broken down into sugar and fiber which work together to regulate blood sugar levels and keep your energy levels consistent. In addition to their role as energy sources, carbs are also essential for maintaining muscle mass, reproductive health, and cognitive function.
The benefits of consuming carbohydrates
When you think of carbohydrates, what comes to mind? Chances are, you think of sugar and processed foods. But did you know that consuming carbohydrates in moderation is necessary for optimal health? Carbohydrates are responsible for providing energy to your body. They also help to form and maintain muscle tissue and help to regulate blood sugar levels. When choosing carbohydrates, make sure to read the nutrition label carefully to ensure you are getting the most benefits from your food choices.
Here are some benefits of consuming carbohydrates:
1. Carbohydrates provide energy that can help you stay active and focused throughout the day.
2. They help to form and maintain muscle tissue.
3. They help to regulate blood sugar levels.
4. They are essential for optimal health and wellbeing.
What are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are the most important type of nutrients for the body because they are the main source of energy for the muscles and brain. Carbohydrates are found in many food items, including vegetables, fruits, grains, and sugars. The main types of carbohydrates include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
There are two types of carbohydrates: simple and complex. Simple carbohydrates are easy to break down into glucose and energy is released quickly. Complex carbohydrates take longer to break down into glucose but release energy over a period of time.
Some foods that contain simple carbohydrates include white sugar, brown sugar, honey, maltose, and lactose. Some foods that contain complex carbohydrates include whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables. Sugars such as sucrose (table sugar) are a type of complex carbohydrate.
The amount of carbohydrates in a food item will appear on the Nutrition Facts label. The amount of carbohydrates in a food item is expressed in grams or calories. The number on the Nutrition Facts label represents the percent of daily value for carbohydrate for a specific food item. The daily value for carbohydrate is based on a 2,000 calorie diet.
The
Types of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients your body needs in order to operate. There are many types of carbohydrates, and all have different nutritional benefits. Here’s a look at some of the most common types of carbohydrates:
Fiber: This type of carbohydrate is found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Fiber helps promote regularity and can help reduce the risk of some types of cancer.
Glucose: Glucose is the most important type of carbohydrate because it’s what your brain and muscles use for energy. You need glucose for basic functions like breathing, moving, and digesting food.
Galactose: Galactose is a type of sugar that’s found in milk, dairy products, and certain vegetables. Galactose can help you feel full longer and may help protect against heart disease.
How Carbohydrates Are Used In The Body
Carbohydrates play an important role in energy production in the body. They are responsible for providing the energy that is needed to carry out everyday tasks. When carbohydrates are consumed, they are broken down into glucose which is then used by the body for energy. The type of carbohydrate that is consumed can have a significant impact on how quickly the glucose is used by the body.
There are two main types of carbohydrates: simple and complex. Simple carbohydrates are those that contain only one sugar molecule. These include sugars such as glucose, fructose, and galactose. Complex carbohydrates contain more than one sugar molecule and these include starches, fiber, and oligosaccharides.
The type of carbohydrate that is consumed can have a significant impact on how quickly the glucose is used by the body. Complex carbohydrates take longer to break down into glucose than simple carbohydrates, which means they provide more sustained energy. This is why athletes often prefer to consume complex carbohydrates during endurance events such as marathons and bike races.
However, there are some drawbacks to consuming complex carbohydrates. They can be harder to digest and can cause spikes in blood sugar levels after consumption.

What Are the Nutrition Facts for Foods?
The nutrition facts for foods list the number of carbohydrates in a food. Carbohydrates are broken down into monosaccharides and disaccharides. Monosaccharides are the simplest type of carbohydrate and include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Disaccharides are composed of two monosaccharides linked together by a sugar molecule. The Nutrition Facts label lists the monosaccharide and disaccharide levels in a food.
The Nutrition Facts label does not list the level of dietary fiber or sugar alcohols in a food. Dietary fiber is found in plant-based foods and can help with digestion. Sugar alcohols are made from sugar molecules but have fewer calories than regular sugar. They are found in some drinks, candies, and granola bars.
The Nutrition Facts label includes a list of dietary minerals, vitamins, and other nutrients in a food. The level of each nutrient is listed as milligrams per serving. Some nutrients cannot be listed on the Nutrition Facts label because they are not considered to be important nutritional factors. These nutrients are calcium, iron, magnesium, zinc, potassium, sodium, and vitamin D.
Why Is There a Difference in Calories on the Label for Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are one of the main sources of energy for the body. When a person eats carbohydrates, the body breaks them down into simple sugar molecules. These sugar molecules are then transported around the body and used as energy. The three types of carbohydrates that are most important for the body are glucose, fructose, and galactose.
The main difference between these three types of carbohydrates is how much they raise blood sugar levels. Glucose is the simplest carbohydrate and it raises blood sugar levels quickly. Fructose and galactose are two other types of carbohydrates and they take longer to raise blood sugar levels. However, they also tend to be more filling than glucose because they contain more calories.
Therefore, when a person looks at the label of a food, they will see different numbers for carbs depending on whether it is glucose, fructose, or galactose. For example, a bag of potato chips may have 20 grams of carbs but only 4 grams of fructose. This means that the potato chips will have a lower number for carbs on the label compared to something like sweetened condensed milk which has 24 grams of carbs but 8 grams of fructose.
What to Do If You Think You’re Having Too Much Sugar or Carbohydrates in Your Diet?
If you’re concerned that your diet might be too high in carbohydrates, here are a few things to keep in mind:
1. Try to estimate how many carbohydrates make up a given food item. This can be difficult, but using online nutrition calculators or tracking your diet using a food diary can help you get a pretty good idea.
2. Consider cutting back on sugary snacks and treats. If you’re trying to cut down on your overall carbohydrate intake, limiting those types of foods can help make a big difference.
3. Avoid processed foods and foods with a lot of added sugar. These items tend to have a lot of carbohydrates in them, and it’s easy to overdo it if you’re eating them on a regular basis.
4. Make sure to get enough fiber in your diet. This important nutrient helps regulate blood sugar levels and can help reduce the number of carb grams you eat overall.
Conclusion
Many people believe that carbohydrates don’t add up, but that’s not always the case. When you’re reading a nutrition label and looking at the carbohydrate percentages, it’s important to take into account all of the information on the label. The percentage on the Nutrition Facts panel is just one piece of information; other factors include how many grams of fiber are in a particular food and how much sugar is in it. If you want to be sure that your carb intake is reasonable, read all of the information on a food’s label!



